LLM的应用开发框架——Langchain
一. Langchain是什么
Langchain 官网文档:https://python.langchain.com/v0.2/docs/introduction/
LLM崛起出现了哪些需求?
• 格式化输出:希望给的输出格式是json、csv、db格式• 输出很长的提示词文本:如何总结一本书的内容?• 多次API调用:两次调用api,前后两次需要结合的• 外部调用:比如需要进行web 搜索• 标准化开发• 快速切换模型:有多个大模型可用,支持代码不变,快速切换二. Langchain支撑LLM的应用
2.1 支持多种LLM
无论是国外的GPT4、LLaMa,还是国内的ChatGLM、Baichuan,都支持调用api和huggingface模型的使用,下面主要介绍HF模型的下载使用。
from huggingface_hub import snapshot_downloadfrom langchain.llms.base import LLM # 指定下载目录(在当前文件夹下)snapshot_download(repo_id="baichuan-inc/Baichuan2-7B-Chat-4bits", local_dir="baichuan-inc/Baichuan2-7B-Chat-4bits")classbaichuan2_LLM(LLM):# 基于本地 Baichuan 自定义 LLM 类 tokenizer:AutoTokenizer=None model:AutoModelForCausalLM=Nonedef__init__(self, model_path: str, dtype = torch.bfloat16):# model_path: Baichuan-7B-chat模型路径# 从本地初始化模型super().__init__()print("正在从本地加载模型...") self.tokenizer =AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_path, trust_remote_code=True) self.model =AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_path, trust_remote_code=True, torch_dtype=dtype, device_map="auto") self.model.generation_config =GenerationConfig.from_pretrained(model_path) self.model = self.model.eval()print("完成本地模型的加载")def_call(self, prompt: str, stop: Optional[List[str]] = None, run_manager: Optional[CallbackManagerForLLMRun] = None, **kwargs: Any):# 重写调用函数 messages =[{"role":"user","content": prompt}]# 重写调用函数 response = self.model.chat(self.tokenizer, messages)return response @propertydef_llm_type(self)->str:return "baichuan2_LLM"2.2 零样本少样本提示
对于LLM来说,尽可能的使用prompt来尝试解决问题,而非直接对LLM进行训练。
因此对于少数据或者没有数据来利用prompt来解决问题:
• zero-shot prompting:直接问模型,最低成本获取答案• few-shot prompting:给模型几个例子,引导它做的更好在Langchain中已经集成了few-shot prompting,如下例子
from langchain.prompts.few_shot importFewShotPromptTemplateexamples =[{"question":"你好吗?","answer":"帅哥,我很好"},{"question":"今天周几?","answer":"帅哥,今天周日"},{"question":"天气好吗?","answer":"帅哥,是的,今天天气很不错"}] example_prompt =PromptTemplate(input_variables=["question","answer"], template="提问: {question}\n回答:{answer}") prompt =FewShotPromptTemplate(examples=examples, example_prompt=example_prompt, suffix="提问: {input}\n", input_variables=["input"])print(prompt.format(input="我怎么这么丑"))# 这里相当于将前缀的这些少样本和当前问题全部放入llm,让其知道前后关系或者学习规则print(llm.predict((prompt.format(input="我怎么这么丑"))))2.3 文档问答
方案:LangChain + ChatGLM,GitHub - chatchat-space/Langchain-Chatchat
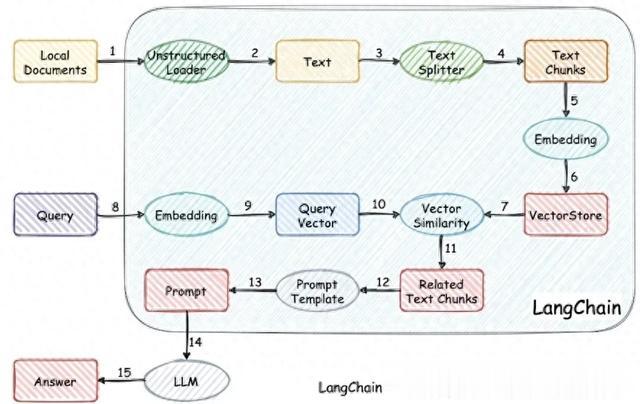
整体流程:
• 本地文档通过Loader读入• 利用文档分割器对其文字进行分割,不然文字太长无法输入llm• 利用Embedding Model(直接利用Huggingface下载相关词嵌入模型)对分割后的文档chunk进行向量化操作• 利用VectorStore(可以选择Chroma或者FAISS作为DB)对向量进行存储• 对于新的query而言,向量化后对Vecorstore进行搜索其相似度高的chunk• 最后将chunk文档同样放入prompt中,输入模型,得到结果Langchain支持的优势:
• 支持相关模块,比如TextSplitter、Loader、Embedding、Vector• 在文档中直接找到相似度最关联的chunk,减少输入llm的文字,从而缩短推理时长从 LangChain + LLM 的流程图可以看出,embedding 的召回率、LLM 的回答能力都会影响到最终回答的准确率。所以,要如果你遇到了 bad case ,你应该先确认这个 bad case 是召回错误,还是模型回答错误。
下面使用庆余年这本书示范的例子,这里的LLM和Embedding模型均来自于Huggingface。
from langchain.indexes.vectorstore importVectorStoreIndexWrapperfrom langchain.text_splitter importRecursiveCharacterTextSplitterfrom langchain_community.vectorstores import FAISSfrom langchain_community.document_loaders importTextLoaderdefload_text_save_index(file_path,index_name): loader =TextLoader(file_path) text_qyn = loader.load() splitter =RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter( chunk_size=100,# 分割出来的文本长度 chunk_overlap=10,# 块之间的重叠文字 length_function=len,# 计算每个块的长度 add_start_index=True# 决定是否在metadata中包含每个块在原始文档中的起始位置) texts = splitter.split_documents(text_qyn)[:100] faiss_db = FAISS.from_documents(texts, hf_embeddings) faiss_db.save_local(os.path.join(local_persist_path,index_name))print('faiss db saved !')defload_index(index_name): index_path = os.path.join(local_persist_path, index_name) faiss_db = FAISS.load_local(index_path,embeddings=hf_embeddings,allow_dangerous_deserialization=True) index =VectorStoreIndexWrapper(vectorstore = faiss_db)return indexfile_path ='庆余年.txt'local_persist_path ='./vector_store'# load_text_save_index(file_path,index_name='庆余年')index = load_index(index_name='庆余年')result = index.query("五竹是谁", llm=llm)print(result)2.4 搜索助手
对于Langchain而言,有专门的Agent模块,其支持对指令进行外部搜索。因此需要申请google搜索的APIkey,这里推荐SerpAPI的key。
from langchain.agents import initialize_agentfrom langchain_community.agent_toolkits.load_tools import load_toolstools = load_tools(['serpapi','llm-math'],llm=llm)print(tools[1].name,tools[1].description)agent = initialize_agent(tools,llm,agent = 'zero-shot-react-description',verbose=True)agent.run('苹果的CEO,他10年后多少岁?')2.5 文章总结
对于一个大型的文章而言,如果直接全部扔给LLM,无疑是会报显存错误的,因此需要将大的文本切分成小的docs,Langchain支持一下三种总结链方式将docs输入给LLM:
• stuff:将所有的docs汇总成一个总的提示直接塞给LLM,这里可能会字数太长而报错。• map_reduce:每个docs 依次输入LLM进行总结,并将每个总结的结果拼接后再次输入LLM作为汇总。• refine:通过循环遍历输入doc并逐步更新其答案来构建响应。对于每个doc,它将所有非文档输入、当前文档和最新的中间答案传递给LLM链以获得新的答案。下面是对URL网页的文章做一个汇总的过程
from langchain_community.document_loaders importUnstructuredURLLoaderfrom langchain.text_splitter importRecursiveCharacterTextSplitterfrom langchain.chains.summarize import load_summarize_chainfrom langchain_core.prompts importPromptTemplatedefload_news(url): text_splitter =RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(# separators=['正文','撰稿'], chunk_size=300, chunk_overlap=10) loader =UnstructuredURLLoader([url]) data = loader.load_and_split(text_splitter)print(f'doc lenth is {len(data)}')return datadefsummary_news(): map_prompt_temp ="""总结这段新闻的内容在50字以内:{text}, 总结:""" ch_prompt =PromptTemplate(template=map_prompt_temp, input_variables=['text']) chain = load_summarize_chain(llm, chain_type='map_reduce', map_prompt=ch_prompt, combine_prompt=ch_prompt)# summary = chain_ch.run(doc) summary = chain.invoke({"input_documents": doc})['output_text']print(summary) # 这里展示的是中文的总结2.6 输出解析
往往我们希望对于LLM生成的结果,能输出成我们预先定义好的格式。下面是对文章指定生成剧本的形式的过程。
from langchain.output_parsers importPydanticOutputParserfrom pydantic importBaseModel,Fieldfrom typing importList# 注意:这里的BaseModel的类的description 不能用中文,因为到template的prompt的时候,会乱码,导致模型不懂描述的是什么classLine(BaseModel):# character:str = Field(description=u"说这句台词的角色名字",) character:str=Field(description=u"The name of the character who said this line",)# content:str = Field(description=u"台词的具体内容,其中不再包含角色的名字") content:str=Field(description=u"The specific content of the line, which no longer contains the character's name")classJuBen(BaseModel):# script: List[Line] = Field(description=u"一段的台词剧本") script:List[Line]=Field(description=u"A talk script")defparse_process(): temp ="""我将给你一段文章,请按照要求把这段文章改写成一个电视剧的剧本。 文章:"{docs}" 要求:"{request}" {output_instructions} """ parser =PydanticOutputParser(pydantic_object=JuBen) prompt =PromptTemplate(template=temp, input_variables=['docs','request'], partial_variables={"output_instructions": parser.get_format_instructions()},# pattern = re.compile('\n')) jb_content = prompt.format_prompt(docs=docs, request="风格大胆悲情,剧本对话角色不少于三个人,以他们的自我介绍为开头")# msg = [HumanMessage(content=jb_content)]# rs = llm.predict_messages(msg) rs = llm(jb_content.to_string()) jb = parser.parse(rs)# chain = jb_prompt | llm | parser# xiangsheng = chain.invoke({# "docs" : docs,# "request" : "风格大胆悲情,剧本对话角色不少于三个人,以他们的自我介绍为开头"# })# print(jb)return jb