CrewAI是一个可以专门用来编排自主 AI 智能体(Autonomous AI Agents) 的Python 框架,你可以把它理解为在代码层面组建一个“虚拟团队”,给每个 Agent 分配特定的角色、目标,让它们协同处理那些单个 LLM 搞不定的复杂任务。
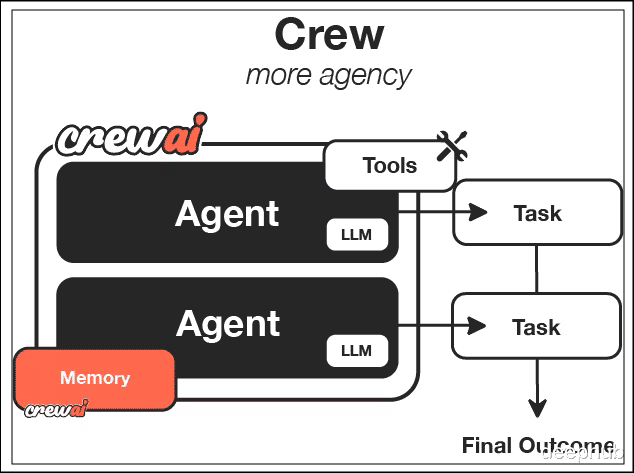
CrewAI 包含以下组件:
Agents 是具体的执行实体,有角色设定和能力边界;Tasks 是具体的任务指令;Crews 是把“人”和事儿撮合到一起的团队容器;Tools 则是 Agent 手里的工具(比如搜索、读文件、调 API等等);Processes 决定了活儿怎么干,比如说是大家排队干(顺序)还是层级汇报(层级)。
CrewA最适合的是那种链条长、环节多的工作流。比如你要搞个深度研报,需要先全网搜集信息,然后整理分析,写初稿,最后润色发布,这种“研究-写作-编辑”的流水线就非常契合。同理商业竞品分析、代码开发流程(设计-编码-测试)或者分工明确的客户支持系统,都是它的强项。
但有几种情况别用:
如果你的任务简单到一次 LLM 调用就能解决,用 CrewAI 就没有必要了而且还会增加复杂度和成本。对实时性要求极高的场景(比如毫秒级响应)也不合适,因为多 Agent 交互本来就慢。还有那种每一步都得让人盯着确认的流程,这种流程自动化程度太低也没必要上 Agent 编排。
安装与配置环境准备很简单,基础包装上就行,如果需要额外的工具集,就把 tools 加上。
# Install CrewAI pip install crewai crewai-tools# For additional tools pip install 'crewai[tools]'
基础示例:搭建内容创作团队下面这段代码展示了如何把 Research Analyst(研究员)、Content Writer(撰稿人)和 Editor(编辑)这三个角色串起来。代码逻辑很简单:定义 Agent,定义 Task,最后塞进 Crew 里跑起来。
注意观察 context 参数,它实现了任务间的数据流转。
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew, Process from crewai_tools import SerperDevTool, WebsiteSearchTool# Initialize tools search_tool = SerperDevTool() web_tool = WebsiteSearchTool()# Create Agents researcher = Agent( role='Research Analyst', goal='Gather comprehensive information on {topic}', backstory='You are an expert researcher with a keen eye for detail and accuracy.', tools=[search_tool, web_tool], verbose=True, allow_delegation=False )writer = Agent( role='Content Writer', goal='Create engaging, well-structured content about {topic}', backstory='You are a skilled writer who transforms research into compelling narratives.', verbose=True, allow_delegation=False )editor = Agent( role='Editor', goal='Refine and polish content to ensure quality and clarity', backstory='You are a meticulous editor with an eye for grammar, style, and flow.', verbose=True, allow_delegation=False )# Define Tasks research_task = Task( description='Research {topic} and gather key facts, statistics, and insights.', expected_output='A comprehensive research report with sources', agent=researcher )writing_task = Task( description='Using the research, write a 500-word blog post about {topic}', expected_output='A well-written blog post in markdown format', agent=writer, context=[research_task] # Depends on research task )editing_task = Task( description='Edit the blog post for grammar, clarity, and engagement', expected_output='A polished, publication-ready blog post', agent=editor, context=[writing_task] )# Create Crew crew = Crew( agents=[researcher, writer, editor], tasks=[research_task, writing_task, editing_task], process=Process.sequential, # Tasks run in order verbose=True )# Execute result = crew.kickoff(inputs={'topic': 'Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare'}) print(result)
进阶示例:软件开发对于更复杂的场景,比如软件开发,可能需要引入层级流程(Hierarchical Process)。这时候会有一个隐藏的 Manager Agent(通常用更强的模型如 GPT-5)来统筹分配任务,而不是简单的线性执行。
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew from crewai_tools import FileReadTool, CodeInterpreterTool# Tools file_tool = FileReadTool() code_tool = CodeInterpreterTool()# Agents with specific expertise architect = Agent( role='Software Architect', goal='Design scalable software architecture for {project}', backstory='Senior architect with 15 years of experience in system design.', verbose=True )developer = Agent( role='Python Developer', goal='Write clean, efficient Python code', backstory='Expert Python developer focused on best practices.', tools=[code_tool], verbose=True )qa_engineer = Agent( role='QA Engineer', goal='Ensure code quality through comprehensive testing', backstory='Detail-oriented QA engineer specializing in test automation.', tools=[code_tool], verbose=True )# Tasks design_task = Task( description='Design architecture for a {project} including component breakdown', expected_output='Detailed architecture document with diagrams', agent=architect )development_task = Task( description='Implement the core functionality based on the architecture', expected_output='Working Python code with documentation', agent=developer, context=[design_task] )testing_task = Task( description='Write and execute unit tests for the developed code', expected_output='Test suite with coverage report', agent=qa_engineer, context=[development_task] )# Hierarchical process with manager agent dev_crew = Crew( agents=[architect, developer, qa_engineer], tasks=[design_task, development_task, testing_task], process=Process.hierarchical, # Manager coordinates tasks manager_llm='gpt-4', # Manager uses GPT-4 verbose=True )result = dev_crew.kickoff(inputs={'project': 'RESTful API for task management'})
进阶功能:异步、人工介入与结构化输出如果你追求性能,异步执行(Asynchronous Execution) 是一个可选项,特别是 IO 密集型任务。
# Run crew asynchronously for better performance result = await crew.kickoff_async(inputs={'topic': 'AI trends'})# Run specific tasks in parallel from crewai import Task task1 = Task(description='Research topic A', agent=researcher, async_execution=True) task2 = Task(description='Research topic B', agent=researcher, async_execution=True)
有些关键节点不能完全信赖 AI,这时候开启 Human-in-the-Loop,Agent 执行到一半会停下来问你要反馈。
agent = Agent( role='Decision Maker', goal='Make strategic decisions', human_input=True # Will prompt for human feedback )
工程化最头疼的是输出格式不可控,CrewAI 支持 Pydantic 模型,强制 Agent 输出结构化数据,这对后续的数据清洗非常有帮助。
from crewai import Task from pydantic import BaseModelclass BlogPost(BaseModel): title: str content: str tags: list[str]task = Task( description='Write a blog post', expected_output='Blog post with title and tags', agent=writer, output_json=BlogPost, # Structured output output_file='output.json' # Save to file )
生态与集成官方内置了一堆工具库,覆盖了搜索(Google/Serper)、文件操作(File/Directory Read)、代码执行(CodeInterpreter)以及各种数据源(PDF, CSV, JSON, GitHub, YouTube)的读取。
模型支持方面利用了 LangChain 的生态,OpenAI, Anthropic, Google Gemini 都能切。想省钱或者数据敏感,用 Ollama 跑本地模型(Llama 3, Mistral)也没问题。
CrewAI vs 其他经常有人问它和 AutoGen 的区别。简单说CrewAI 像是管理严密的正规军,强调角色(Role)和流程(Process);AutoGen 更像是一个聊天室,Agent 之间通过对话来解决问题,更灵活但也更难控制。至于 LangGraph,那是更底层的图编排工具,控制粒度极细,但上手门槛高。你可以理解为CrewAI 是在 LangChain 之上做了很好的封装,用起来简单。
补充规划、记忆与安全新版本(0.30+)加入了 Planning Mode,Agent 开干前会先生成个计划书(现在Agent基本上都会有计划了)。记忆系统也升级了:支持短期记忆(本次执行内)、长期记忆(跨执行持久化)甚至实体记忆(记住具体的人和事)。
如果你需要监控整个 Crew 的运行状态,可以开启 Telemetry,导出 JSON 格式的日志做分析。
总结CrewAI 在处理角色分工明确、流程复杂的知识型工作时表现非常出色。如果你是初学者:先别整太复杂的流程,2-3 个 Agent 起步,把目标定死,用 Pydantic 锁死输出格式,把缓存开起来。等熟悉了 Agent 的操作,再上复杂的层级结构和记忆系统。
https://avoid.overfit.cn/post/03c0bdbc21254d52b80f170a0fa2c567